RIO DE JANEIRO, BRAZIL – The District Sample Household Survey (Pnad do DF), released on May 9 by the Planning Company of the Federal District (Codeplan), presented the socio-economic profile of the federal capital in 2021, based on data obtained from all administrative regions.
The highest percentage of the economically active population (aged 14 or more) was seen in the lower class, covering 60.7% of this group. In the other groups, the percentage was always close to 58%.
The average age of the inhabitants of these households varied from 30.6 years (low-income families) to 37.6 years (high-income families). The households in the upper-middle and lower-middle-income brackets presented an average age of 36.4 years and 33.6 years, respectively.
POPULATION AND SAMPLE
The population of the Federal District is estimated at 3,010,881 people, according to Codeplan. Most of them (989,578) are lower-middle class, followed by lower class (852,217); upper-middle class (624,654); and upper class (544,432).
The sample, which served as the basis for the 2021 survey, was made in 30,888 households. The biggest sample part is high-income households (11,501 households, with an average household income of R$14,753.85 – US$2,860). The sample of low-income domiciles is 7,563 (these present an average domiciliary income of R$2,644.96).
The upper-middle-income sample includes 7,580 households. This group has an average household income of R$6,517.82. The sample of lower-middle-income households comprises 4,244 homes with an average income of R$2,644.96.
In July 2021, the average monthly gross income from the main job of a high-income household was R$8,237. The average for low-income households was R$1,757. For upper-middle and lower-middle-income households, it was R$3,747 and R$2,335, respectively.
CHARACTERISTICS
Concerning the characteristics of the residents, most of the Federal District (DF) population is black and mixed-race (57.4% of the total number of residents). The research also shows that the lower the household income, the higher the presence of this group: 68.1% of the low-income people are black and mixed race, a percentage that drops to 38.8% when the cut considers the residents who belong to the upper class.
Public educational institutions are more frequented by low-income people between 4 and 24 years old (88.1%) and those from the lower middle class (80.2%). The percentage drops to 56% in the case of upper-middle-income residents and 27.5% among the high-income ones.
The upper class is the one that has managed to finish higher education the most. The average of people aged 25 or more who have completed higher education among those in the sample is 36.3%. Among the upper class, the percentage rises to 76.9%. When the cut-off includes lower-class residents, the percentage is only 14.4%.
A similar situation is observed in the population with a private health plan: 75.3% of the upper-class residents have access to this type of service, while only 11.8% of the low-income people use health plans.
Concerning gender identity and sexual orientation among people aged 18 and older, it is in the group with high income where it is found more of those who declare themselves to be LGBQTI+. The survey reveals that 5.5% of the wealthiest declare themselves as such. This percentage varies between 3% and 4.3% in the other income groups.
DISPLACEMENT
While high-income residents are those who most use cars to go to work (84.5%, compared to 32.8% with low incomes, use cars for this purpose), it is the lower class who most use buses to go to work (52.9%, a percentage that falls to 11.7% among high-income residents).
Also, according to Codeplan’s survey, 87.8% of the residents with the highest incomes have a national driver’s license, a document held by only 44.9% of the low-income residents.
The commuting time is longer for the lower and lower-middle class, causing about 36% of the residents belonging to this group to take more than 45 minutes in traffic. Among the upper middle income, this percentage drops to 17.4%, and among the high income, it is 7.2%.
Most upper-class residents work in the Plano Piloto (70.8%). It is also the high-income ones who work and live in the same administrative region (53.5%).
SERVICES
Regular policing and tree-lined and paved streets favor more the places where people with higher incomes live and less the places where people with lower incomes live.
The same is seen in the case of access to services such as pay-TV (accessible to 67% of high-income households and 18% of low-income households) and streaming (online movie and music services, among others), which is accessible to 80% of high-income households and 44.2% of low-income households.
On the other hand, the Internet has been practically universalized, being accessible to 99% of the entire population.
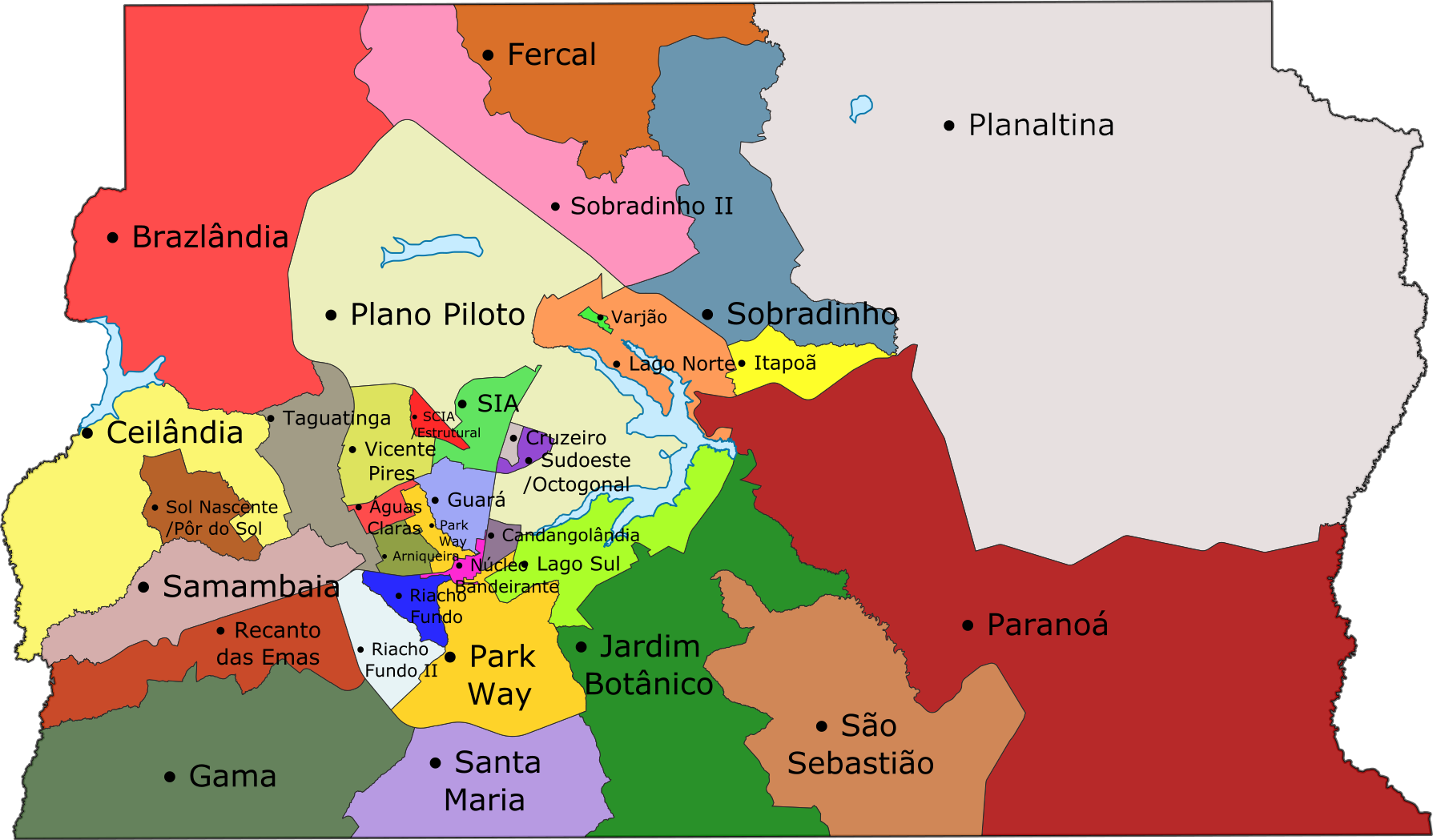
The high-income regions are Águas Claras, Jardim Botânico, Lago Norte, Lago Sul, Park Way, Plano Piloto, and Sudoeste/Octogonal. The upper-middle-income areas are Arniqueira, Candangolândia, Cruzeiro, Guará, Núcleo Bandeirante, Setor de Indústria e Abastecimento, Sobradinho, Taguatinga, and Vicente Pires.
The low-middle-income areas are, according to the Codeplan study, Ceilândia, Gama, Riacho Fundo, Samambaia, Santa Maria and Sobradinho II; and the low-income areas are Brazlândia, Fercal, Itapoã, Paranoá, Planaltina, Recanto das Emas, Riacho Fundo II, São Sebastião, Setor Complementar de Indústria e Abastecimento-Estrutural, Sol Nascente/Pôr do Sol, and Varjão.
With information from Agência Brasil

