During a Friday event, Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro signed decrees to advance his plan to annex part of Guyana, addressing a crowd of supporters and military personnel.
The decrees aim to formalize statements made on Tuesday.
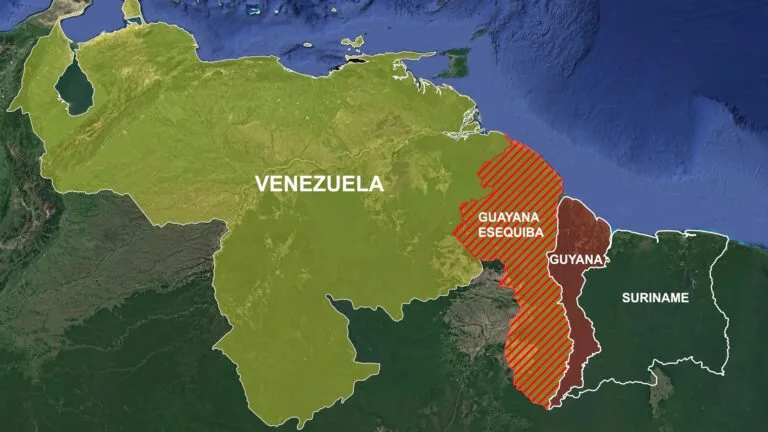
These decrees include several key actions. Firstly, they establish a new state called Guiana Esequiba.
Secondly, they introduce a revised map of Venezuela, now including the disputed area.
Additionally, the decrees open a new division of the state oil company PDVSA to operate in this region.
They also allow for mining licenses and create a Comprehensive Defense Zone in the new area.
Moreover, Maduro has formed a high commission tasked with defending and reclaiming Guiana Esequiba.
He has instructed this commission to develop a long-term strategy, targeting completion by 2030 or later.
This strategy directly relates to the annexation plans. Maduro appointed Delci Rodriguez to lead this commission.
The background of this issue stretches over a century. Venezuela and Guyana have long disputed the Esequibo territory, a region rich in oil and minerals.
Currently, Guyana administers this 160,000 km² area, about the size of Florida or Tunisia.
The conflict intensified after ExxonMobil discovered significant oil reserves there. Guyana’s decision to allow foreign companies to explore these reserves further heightened tensions.
Venezuela asserts that the Esequibo River is the rightful border, referencing its colonial history under Spain in 1777.
They refer to the 1966 Geneva Agreement, which was signed before Guyana’s independence from the UK.
This agreement aimed for a negotiated resolution and nullified an 1899 ruling that set current boundaries.
Guyana, however, upholds the 1899 ruling and seeks its validation by the International Court of Justice.
Background
Venezuela’s annexation efforts mix historical claims with modern geopolitical interests.
Maduro reignited a century-old dispute, showing how colonial-era boundaries still affect today’s international relations.
The region’s rich resources, like oil and minerals, increase its importance.
The world’s reaction is key.
Such disputes often get global attention and action. The UN and International Court of Justice might play a major role in finding a peaceful solution.
Venezuela’s move is similar to other territorial disputes, for example in the South China Sea.
Both involve resources and strategic locations. Yet, the Venezuela-Guyana issue is mostly bilateral, simplifying negotiations.
The 1966 Geneva Agreement and the 1899 ruling are important in this conflict. They show how hard it is to match past deals with current laws and norms.
This situation highlights the need for new legal frameworks for old colonial issues.
Maduro’s creation of a new state and map change is a strong move. But, it could further isolate Venezuela, which already faces political and economic troubles.
Guyana’s position, backed by legal rulings, supports the rule of law against unilateral acts.
In summary, the Venezuela-Guyana dispute shows the complexity of boundary conflicts. It involves historical problems, resource rivalry, and geopolitical factors.
Resolving it will need careful talks, balancing history with modern international legal standards.

