Twitter CEO Elon Musk made history this Friday in favor of transparency.
In April, Twitter released some of its source code for public inspection, including its controversial algorithm to recommend tweets on users’ timelines.
On GitHub, Twitter posted two repositories containing much of the company’s code that make many parts of the social network work, including the mechanism Twitter uses to control which tweets users see in the “For You” timeline.

In the past, this algorithm was heavily criticized by social network users because it suppressed right-wing tweets and trends and promoted left-wing ones.
This was pure speculation until Elon Musk bought the company and confirmed, through the #TwitterFiles, that this was the case.
According to the CEO of Tesla and SpaceX, he completely changed the source code within weeks of taking control of Twitter.
Now, he will make it public to prove that he did it in a historic step towards transparency.
In a Twitter Spaces session this Friday, Musk clarified:
“Our initial release of the so-called algorithm will be pretty embarrassing, and people will find a lot of bugs, but we will fix them very quickly.”
“Even if you disagree with something, at least you’ll know why it’s there and that you’re not being secretly manipulated… ”
“The analog, here, that we’re aiming for is the great example of Linux as an open source operating system…”
“One can, in theory, discover many exploits for Linux.”
“In reality, what happens is that the community identifies and fixes those exploits,” he explained.
He clarified that these publications do not include the code that drives Twitter’s ad recommendations.
This information must be kept confidential due to contractual issues with clients who buy advertising on social networks.
In addition, while showing how the algorithm operates to create the recommendation page, for the time being, Twitter did not publish the data used to train the algorithm, as it could compromise users’ personal information.
“We excluded any code that would compromise user safety and privacy or the ability to protect our platform from bad actors, including undermining our efforts to combat child sexual exploitation and manipulation,” he said.
“We’re going to be looking for suggestions, not just about bugs, but also about how the algorithm should work,” Musk said at the Spaces session.
“It’s going to be an evolving process.”
“I wouldn’t expect it to be a continuous upward movement … but we’re very open to what might improve the user experience,” he concluded.
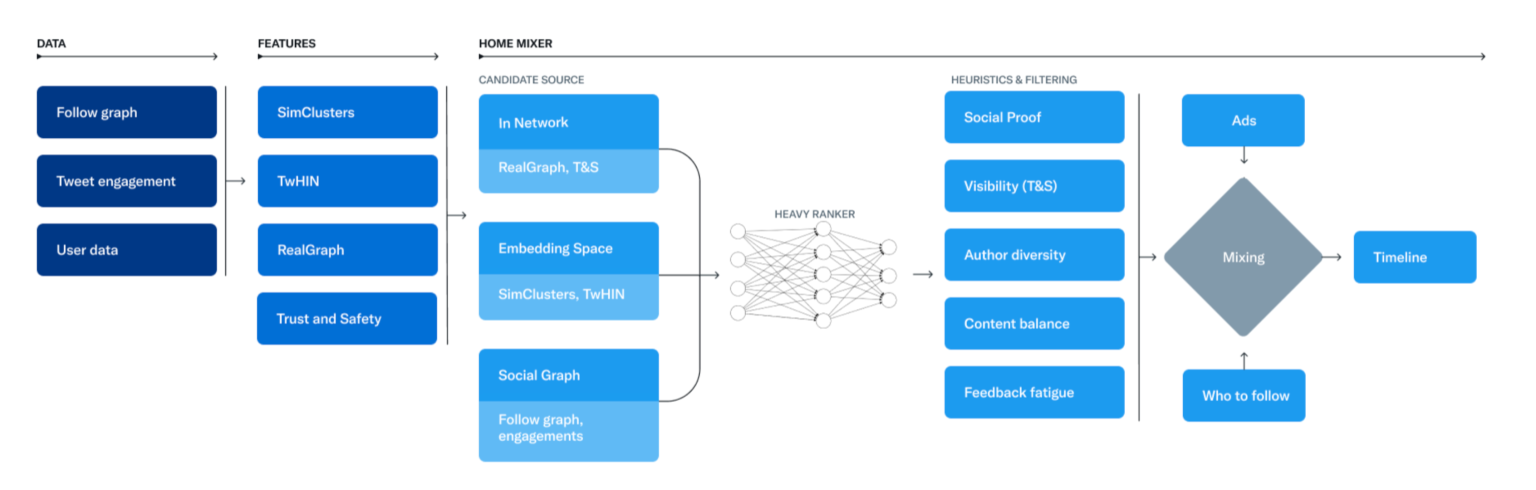
At first glance, the algorithm is quite complex but not necessarily surprising from a technical standpoint.
It is composed of multiple models, including one that detects “Not Safe For Work,” violent or abusive content, then determines the likelihood that a Twitter user will interact with another user based on that tweet and calculates the “reputation” that post will have to appear or not appear among the recommendations one reads on their home page.
The “For You” page is populated by tweets from people you follow, but also by tweets they have liked, retweeted, or even tweets from people who are followed by people you follow. This mass of publications is sorted by this “reputation”.
It was always known that tweets were ranked based on some score, but now we know what it is based on.
The algorithm inspects the content of the tweet and looks for keywords such as “death”, “kill”, “pornography”, and “suicide”, among others.
It also has a sophisticated code that allows it to “read in context” and interpret if the tweet is abusive against another person.
There are no findings of keywords related to extremist issues or vaccines, or Covid-19, something that Elon Musk eliminated because it was previously impossible to post a tweet on these topics without it disappearing from the face of Twitter.
But if there are “tags” that are used to identify a tweet as coming from a “Democrat”, a “Republican”, or an “important” (“power”) user.
There is even a tag indicating whether a tweet came from Elon Musk.
The tycoon mentioned in the space that they are looking for a replacement for this algorithm part.
“I don’t like putting tags on people’s tweets; we’re looking at how not to do that anymore,” he mentioned.
Several neural networks are responsible for ranking tweets and recommending accounts to follow. At the same time, a filtering component hides tweets to, by Twitter’s explanation, “support legal compliance, improve product quality, increase user trust, protect revenue through visible and hard filtered product treatments and coarse-grained top-down ranking.”
As can be seen from the algorithm, Twitter attempts to extract the “best” 1,500 tweets out of the millions that rank to appear on the “For You” page.
In addition, this timeline consists of 50% of tweets from people you follow and 50% from people you don’t follow, emphasizing news, with no preference of which medium; only verified or blue accounts are prioritized.
The classification is achieved with a neural network of almost 48 million parameters continuously trained on tweets’ interactions to optimize positive engagement.
For example, likes, retweets, and replies, but also the time it takes to read a tweet, if, after seeing that tweet, you go to see the user, the time that passes between liking two tweets from the same user, or even the amount of time you spend viewing their images and videos.
With information from La Derecha Diario

